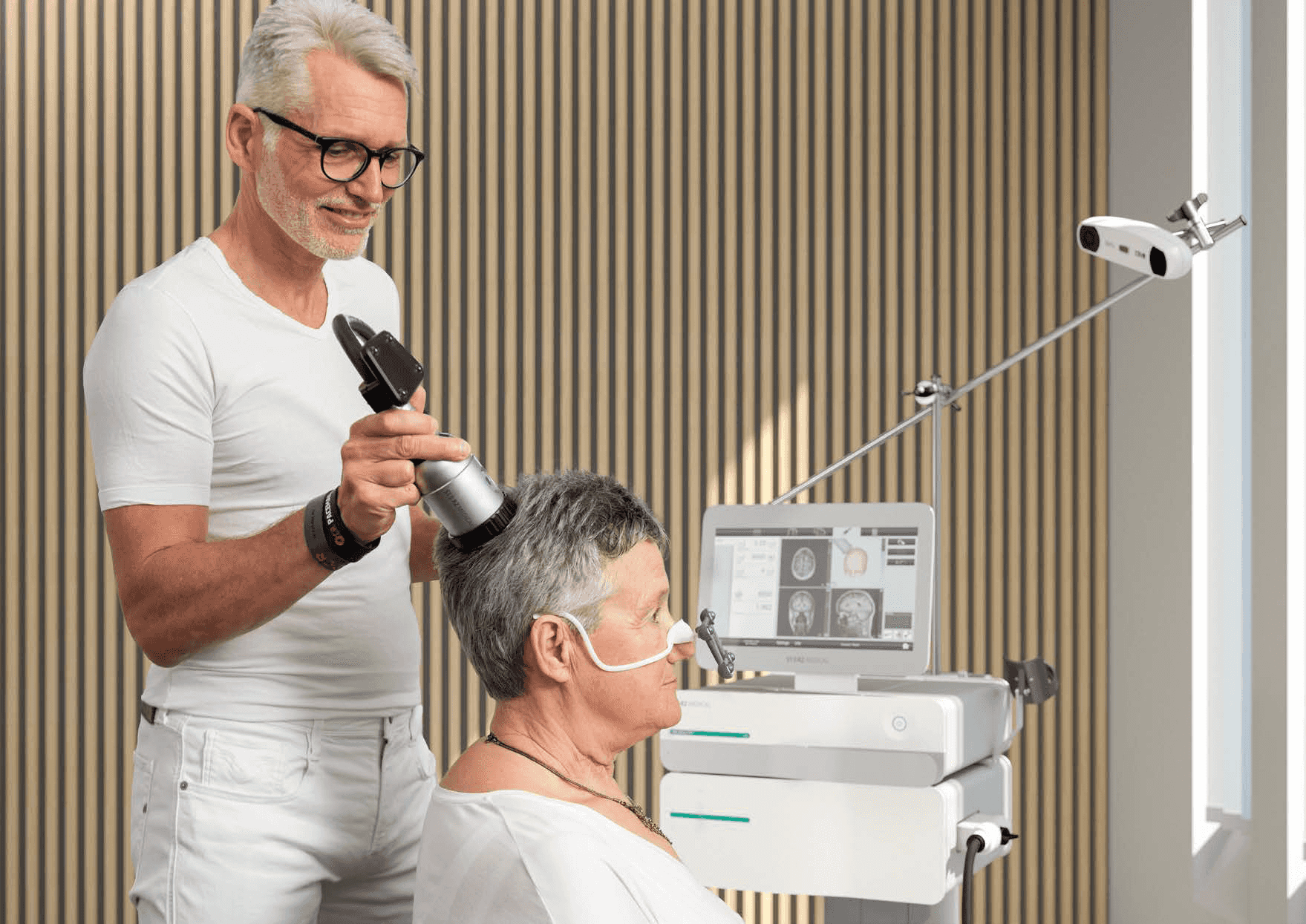
Dementia diagnosis
Diagnosis of dementia includes:
- Medical evaluation.
- Patient and family history.
- Neurological examination.
- Neuropsychological testing.
- Brain imaging (e.g., MRI).
- Laboratory testing to rule out other possible causes.
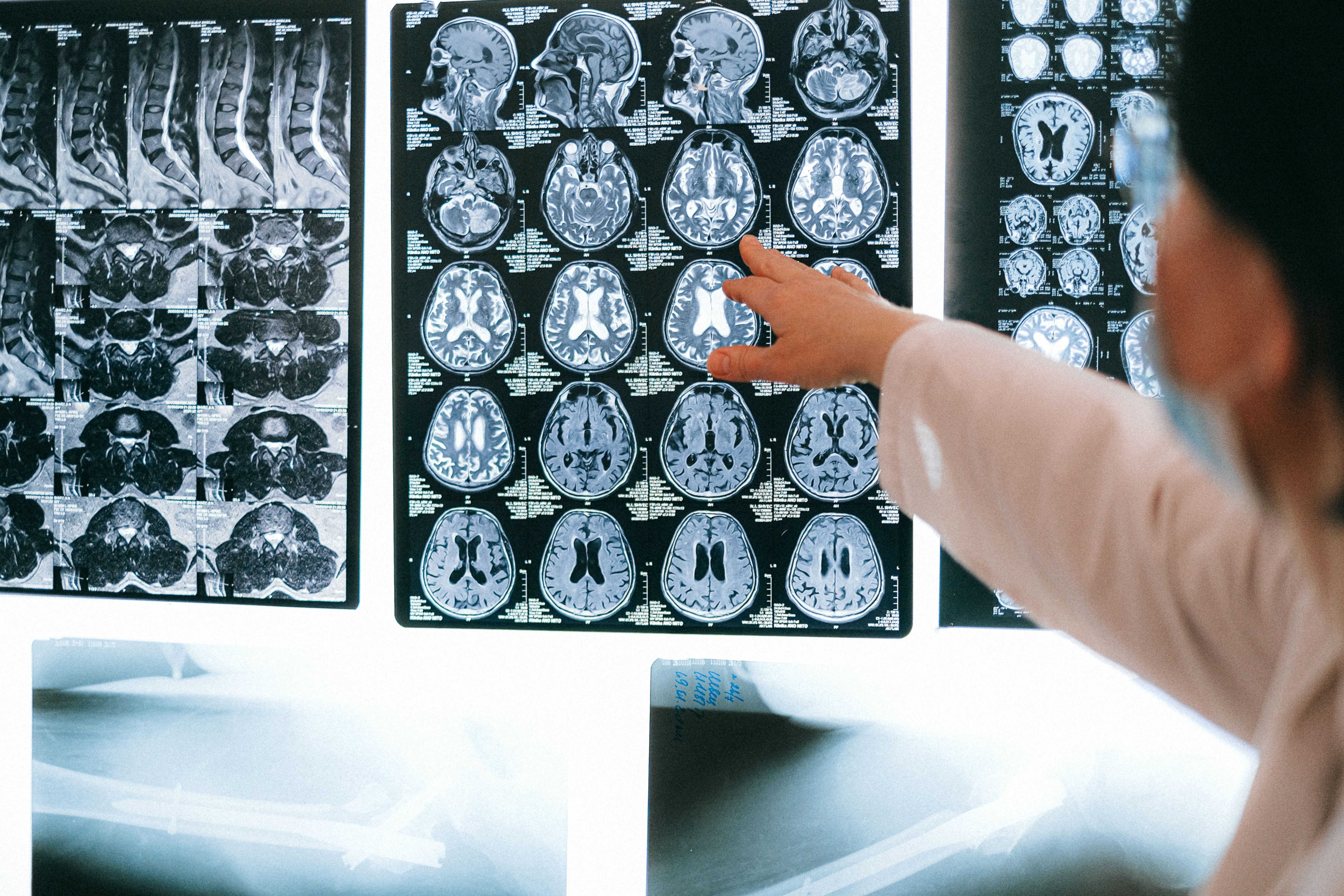
Dementias are not homogeneous and have different varieties, symptoms, and symptoms. Here are some types of dementia:
- Alzheimer's dementia is the most common form of dementia and is caused by the degeneration and death of brain cells. The characteristic symptoms of dementia, in this case, are: progressive memory loss, problems with thinking, disorientation in time and space, and difficulties in performing everyday activities.
- Vascular dementia: is caused by vascular disorders of the brain, such as: stroke or atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries. The diagnosis of dementia, in this case, is based on symptoms, which may include: sudden memory lapses, memory loss, trouble concentrating, confusion, and difficulty speaking.
- Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a type of dementia associated with damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. It is characterized by personality changes, impulse control difficulties, emotional disturbances, decreased empathy, loss of initiative, and problems in planning and making decisions.
- ODementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of dementia associated with structures in the brain called Lewy bodies. Symptoms include fluctuations in attention, hallucinations, sleep disturbances, muscle stiffness, and memory loss.
Diagnosis of dementia includes:
ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia. It cannot be cured. The number of people suffering from Alzheimer's disease continues to grow, with approximately 33 million worldwide now affected. Patients suffer from memory loss, have problems with orientation, and can no longer function independently in everyday life. Many patients, especially in the early stages of dementia, also struggle with depression. This significantly reduces the quality of life of people affected by this disease and their relatives. The progressive loss of neurons causes the clinical symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. The result is a shrinkage of the brain, especially the cerebral cortex. As a result of neuronal atrophy, information transmission and processing points between the nerves are also degraded. These disorders are the cause of memory loss. According to current knowledge, the factor causing Alzheimer's disease is harmful protein molecules formed outside the nerve cells and impairing their work. One of these molecules, beta-amyloid, builds up in the brain of an Alzheimer's patient and gets deposited there. The so-called amyloid plaques are creating, resulting in a deterioration of blood circulation and, consequently, disturbances in the supply of oxygen and energy to the brain.